 在 TensorFlow.org 上檢視 在 TensorFlow.org 上檢視
|
 在 Google Colab 中執行 在 Google Colab 中執行
|
 在 GitHub 上檢視原始碼 在 GitHub 上檢視原始碼
|
 下載筆記本 下載筆記本
|
API 文件: tf.RaggedTensor tf.ragged
設定
!pip install --pre -U tensorflow
import math
import tensorflow as tf
總覽
您的資料有許多種形狀;您的張量也應該如此。「參差不齊張量」是 TensorFlow 中巢狀可變長度清單的對等項目。它們讓您能夠輕鬆儲存和處理形狀不一致的資料,包括:
- 可變長度特徵,例如電影中的演員組合。
- 可變長度循序輸入批次,例如句子或影片片段。
- 階層式輸入,例如細分為章節、段落、句子和單字的文字文件。
- 結構化輸入中的個別欄位,例如通訊協定緩衝區。
您可以使用參差不齊張量執行的操作
超過一百個 TensorFlow 運算支援參差不齊張量,包括數學運算 (例如 tf.add 和 tf.reduce_mean)、陣列運算 (例如 tf.concat 和 tf.tile)、字串操控運算 (例如 tf.strings.substr)、控制流程運算 (例如 tf.while_loop 和 tf.map_fn) 以及許多其他運算。
digits = tf.ragged.constant([[3, 1, 4, 1], [], [5, 9, 2], [6], []])
words = tf.ragged.constant([["So", "long"], ["thanks", "for", "all", "the", "fish"]])
print(tf.add(digits, 3))
print(tf.reduce_mean(digits, axis=1))
print(tf.concat([digits, [[5, 3]]], axis=0))
print(tf.tile(digits, [1, 2]))
print(tf.strings.substr(words, 0, 2))
print(tf.map_fn(tf.math.square, digits))
還有許多方法和運算專用於參差不齊張量,包括工廠方法、轉換方法和值對應運算。如需支援運算的清單,請參閱 tf.ragged 套件說明文件。
許多 TensorFlow API 都支援參差不齊張量,包括 Keras、資料集、tf.function、SavedModel 和 tf.Example。如需詳細資訊,請查看下方的「TensorFlow API」章節。
與一般張量一樣,您可以使用 Python 樣式的索引編製來存取參差不齊張量的特定切片。如需詳細資訊,請參閱下方的「索引編製」章節。
print(digits[0]) # First row
print(digits[:, :2]) # First two values in each row.
print(digits[:, -2:]) # Last two values in each row.
與一般張量相同,您可以使用 Python 算術和比較運算子來執行元素級運算。如需詳細資訊,請查看下方的「多載運算子」章節。
print(digits + 3)
print(digits + tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2, 3, 4], [], [5, 6, 7], [8], []]))
如果您需要對 RaggedTensor 的值執行元素級轉換,則可以使用 tf.ragged.map_flat_values,此函式接受一個函式以及一或多個引數,並套用該函式來轉換 RaggedTensor 的值。
times_two_plus_one = lambda x: x * 2 + 1
print(tf.ragged.map_flat_values(times_two_plus_one, digits))
參差不齊張量可以轉換為巢狀 Python list 和 NumPy array
digits.to_list()
digits.numpy()
建構參差不齊張量
建構參差不齊張量最簡單的方式是使用 tf.ragged.constant,此函式會根據指定的巢狀 Python list 或 NumPy array 建構 RaggedTensor
sentences = tf.ragged.constant([
["Let's", "build", "some", "ragged", "tensors", "!"],
["We", "can", "use", "tf.ragged.constant", "."]])
print(sentences)
paragraphs = tf.ragged.constant([
[['I', 'have', 'a', 'cat'], ['His', 'name', 'is', 'Mat']],
[['Do', 'you', 'want', 'to', 'come', 'visit'], ["I'm", 'free', 'tomorrow']],
])
print(paragraphs)
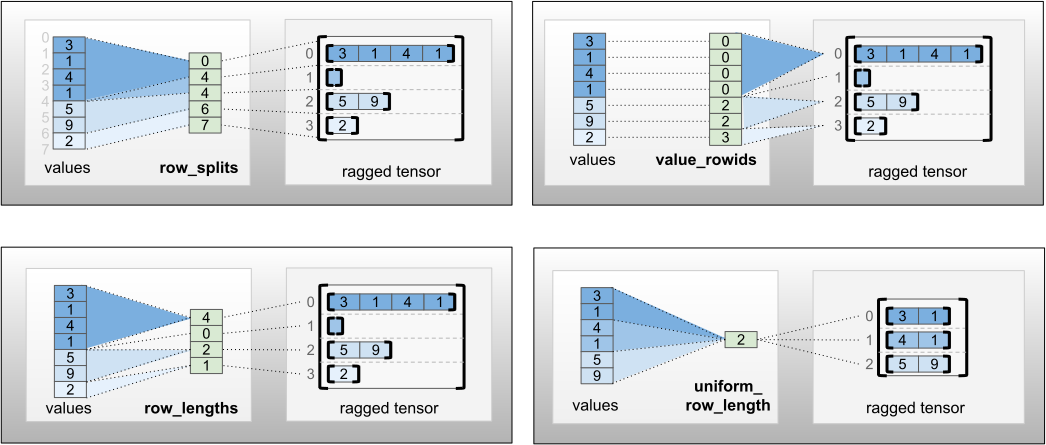
參差不齊張量也可以透過配對扁平「值」張量與「列分割」張量來建構,列分割張量會指出這些值應如何分割成列,方法是使用工廠類別方法,例如 tf.RaggedTensor.from_value_rowids、tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_lengths 和 tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits。
tf.RaggedTensor.from_value_rowids
如果您知道每個值所屬的列,則可以使用 value_rowids 列分割張量建構 RaggedTensor
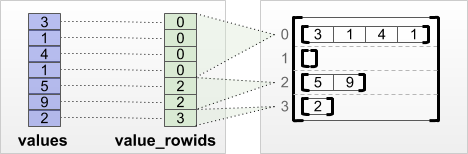
print(tf.RaggedTensor.from_value_rowids(
values=[3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2],
value_rowids=[0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 3]))
tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_lengths
如果您知道每列的長度,則可以使用 row_lengths 列分割張量
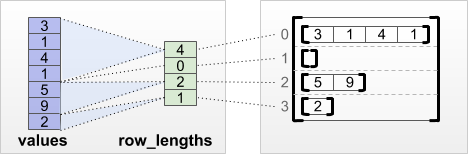
print(tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_lengths(
values=[3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2],
row_lengths=[4, 0, 2, 1]))
tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits
如果您知道每列的起點和終點索引,則可以使用 row_splits 列分割張量
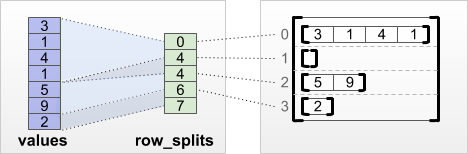
print(tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(
values=[3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2],
row_splits=[0, 4, 4, 6, 7]))
如需工廠方法的完整清單,請參閱 tf.RaggedTensor 類別說明文件。
您可以儲存在參差不齊張量中的內容
與一般 Tensor 相同,RaggedTensor 中的值都必須具有相同的類型;且值都必須位於相同的巢狀深度 (張量的「等級」)
print(tf.ragged.constant([["Hi"], ["How", "are", "you"]])) # ok: type=string, rank=2
print(tf.ragged.constant([[[1, 2], [3]], [[4, 5]]])) # ok: type=int32, rank=3
try:
tf.ragged.constant([["one", "two"], [3, 4]]) # bad: multiple types
except ValueError as exception:
print(exception)
try:
tf.ragged.constant(["A", ["B", "C"]]) # bad: multiple nesting depths
except ValueError as exception:
print(exception)
範例使用案例
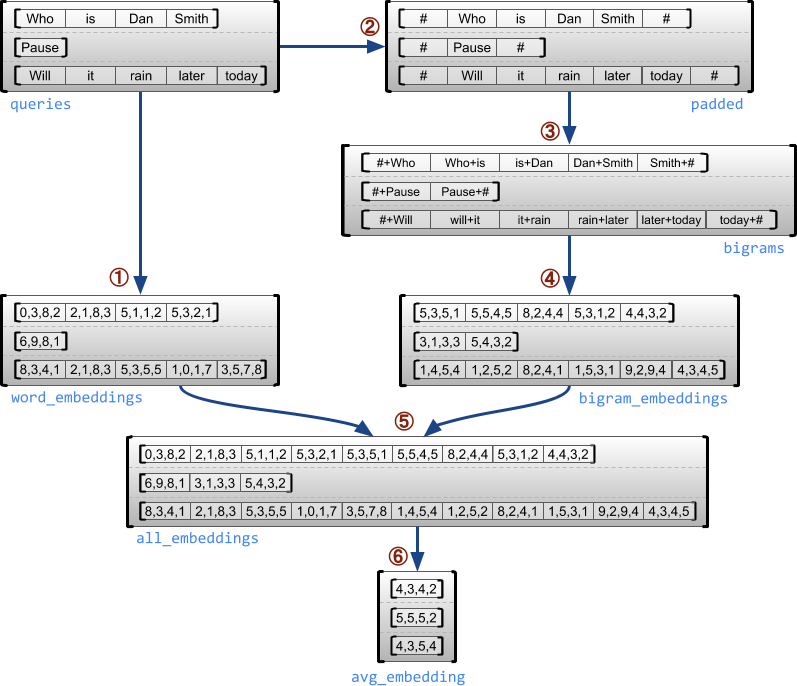
下列範例示範如何使用 RaggedTensor 為一批可變長度查詢建構和合併單字母組和雙字母組嵌入,方法是針對每個句子的開頭和結尾使用特殊標記。如需此範例中所用運算的詳細資訊,請查看 tf.ragged 套件說明文件。
queries = tf.ragged.constant([['Who', 'is', 'Dan', 'Smith'],
['Pause'],
['Will', 'it', 'rain', 'later', 'today']])
# Create an embedding table.
num_buckets = 1024
embedding_size = 4
embedding_table = tf.Variable(
tf.random.truncated_normal([num_buckets, embedding_size],
stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(embedding_size)))
# Look up the embedding for each word.
word_buckets = tf.strings.to_hash_bucket_fast(queries, num_buckets)
word_embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_table, word_buckets) # ①
# Add markers to the beginning and end of each sentence.
marker = tf.fill([queries.nrows(), 1], '#')
padded = tf.concat([marker, queries, marker], axis=1) # ②
# Build word bigrams and look up embeddings.
bigrams = tf.strings.join([padded[:, :-1], padded[:, 1:]], separator='+') # ③
bigram_buckets = tf.strings.to_hash_bucket_fast(bigrams, num_buckets)
bigram_embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_table, bigram_buckets) # ④
# Find the average embedding for each sentence
all_embeddings = tf.concat([word_embeddings, bigram_embeddings], axis=1) # ⑤
avg_embedding = tf.reduce_mean(all_embeddings, axis=1) # ⑥
print(avg_embedding)
參差不齊和一致維度
「參差不齊維度」是指切片長度可能不同的維度。例如,rt=[[3, 1, 4, 1], [], [5, 9, 2], [6], []] 的內部 (欄) 維度是參差不齊的,因為欄切片 (rt[0, :]、...、rt[4, :]) 的長度不同。切片長度都相同的維度稱為「一致維度」。
參差不齊張量的最外層維度永遠是一致的,因為它是由單一切片組成 (因此,不可能出現不同的切片長度)。其餘維度可能是參差不齊或一致的。例如,您可以使用形狀為 [num_sentences, (num_words), embedding_size] 的參差不齊張量儲存一批句子中每個單字的字詞嵌入,其中 (num_words) 周圍的括號表示該維度是參差不齊的。
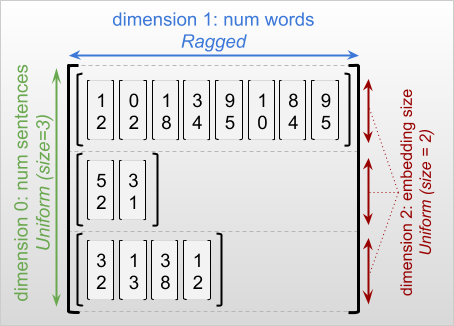
參差不齊張量可能有多個參差不齊維度。例如,您可以使用形狀為 [num_documents, (num_paragraphs), (num_sentences), (num_words)] 的張量儲存一批結構化文字文件 (同樣地,括號用於表示參差不齊維度)。
與 tf.Tensor 相同,參差不齊張量的「等級」是其維度的總數 (包括參差不齊維度和一致維度)。「可能參差不齊張量」是指可能是 tf.Tensor 或 tf.RaggedTensor 的值。
在描述 RaggedTensor 的形狀時,慣例上會以括號括住參差不齊維度。例如,如您在上方看到的,儲存一批句子中每個單字的字詞嵌入的 3D RaggedTensor 形狀可以寫成 [num_sentences, (num_words), embedding_size]。
RaggedTensor.shape 屬性會傳回 RaggedTensor 的 tf.TensorShape,其中參差不齊維度的大小為 None
tf.ragged.constant([["Hi"], ["How", "are", "you"]]).shape
方法 tf.RaggedTensor.bounding_shape 可用於尋找指定 RaggedTensor 的緊密外框形狀
print(tf.ragged.constant([["Hi"], ["How", "are", "you"]]).bounding_shape())
參差不齊與稀疏
不應將參差不齊張量視為一種稀疏張量。特別是,稀疏張量是「tf.Tensor 的效率編碼」,可採用精簡格式為相同的資料建模;但參差不齊張量是「tf.Tensor 的擴充」,可為更廣泛的資料類別建模。在定義運算時,此差異至關重要
- 將運算套用至稀疏或密集張量應始終產生相同的結果。
- 將運算套用至參差不齊或稀疏張量可能會產生不同的結果。
做為示範範例,請考量如何針對參差不齊張量與稀疏張量定義陣列運算,例如 concat、stack 和 tile。串連參差不齊張量會聯結每列,以形成長度組合的單列

ragged_x = tf.ragged.constant([["John"], ["a", "big", "dog"], ["my", "cat"]])
ragged_y = tf.ragged.constant([["fell", "asleep"], ["barked"], ["is", "fuzzy"]])
print(tf.concat([ragged_x, ragged_y], axis=1))
但是,串連稀疏張量相當於串連對應的密集張量,如下列範例所示 (其中 Ø 表示遺漏值)
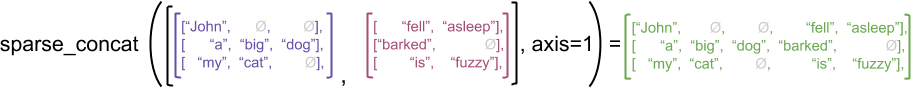
sparse_x = ragged_x.to_sparse()
sparse_y = ragged_y.to_sparse()
sparse_result = tf.sparse.concat(sp_inputs=[sparse_x, sparse_y], axis=1)
print(tf.sparse.to_dense(sparse_result, ''))
如需另一個範例來說明此區別為何很重要,請考量運算 (例如 tf.reduce_mean) 的「每列平均值」定義。對於參差不齊張量,列的平均值是列值的總和除以列的寬度。但對於稀疏張量,列的平均值是列值的總和除以稀疏張量的整體寬度 (大於或等於最長列的寬度)。
TensorFlow API
Keras
tf.keras 是 TensorFlow 用於建構及訓練深度學習模型的高階 API。參差不齊張量可以做為 Keras 模型的輸入傳遞,方法是在 tf.keras.Input 或 tf.keras.layers.InputLayer 上設定 ragged=True。參差不齊張量也可以在 Keras 層之間傳遞,並由 Keras 模型傳回。下列範例顯示使用參差不齊張量訓練的玩具 LSTM 模型。
# Task: predict whether each sentence is a question or not.
sentences = tf.constant(
['What makes you think she is a witch?',
'She turned me into a newt.',
'A newt?',
'Well, I got better.'])
is_question = tf.constant([True, False, True, False])
# Preprocess the input strings.
hash_buckets = 1000
words = tf.strings.split(sentences, ' ')
hashed_words = tf.strings.to_hash_bucket_fast(words, hash_buckets)
# Build the Keras model.
keras_model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[None], dtype=tf.int64, ragged=True),
tf.keras.layers.Embedding(hash_buckets, 16),
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(32, use_bias=False),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(32),
tf.keras.layers.Activation(tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
keras_model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop')
keras_model.fit(hashed_words, is_question, epochs=5)
print(keras_model.predict(hashed_words))
tf.Example
tf.Example 是 TensorFlow 資料的標準 protobuf 編碼。以 tf.Example 編碼的資料通常包含可變長度特徵。例如,下列程式碼定義一批四個具有不同特徵長度的 tf.Example 訊息
import google.protobuf.text_format as pbtext
def build_tf_example(s):
return pbtext.Merge(s, tf.train.Example()).SerializeToString()
example_batch = [
build_tf_example(r'''
features {
feature {key: "colors" value {bytes_list {value: ["red", "blue"]} } }
feature {key: "lengths" value {int64_list {value: [7]} } } }'''),
build_tf_example(r'''
features {
feature {key: "colors" value {bytes_list {value: ["orange"]} } }
feature {key: "lengths" value {int64_list {value: []} } } }'''),
build_tf_example(r'''
features {
feature {key: "colors" value {bytes_list {value: ["black", "yellow"]} } }
feature {key: "lengths" value {int64_list {value: [1, 3]} } } }'''),
build_tf_example(r'''
features {
feature {key: "colors" value {bytes_list {value: ["green"]} } }
feature {key: "lengths" value {int64_list {value: [3, 5, 2]} } } }''')]
您可以使用 tf.io.parse_example 剖析此編碼資料,此函式接受序列化字串的張量和特徵規格字典,並傳回將特徵名稱對應至張量的字典。若要將可變長度特徵讀取至參差不齊張量,您只需在特徵規格字典中使用 tf.io.RaggedFeature 即可
feature_specification = {
'colors': tf.io.RaggedFeature(tf.string),
'lengths': tf.io.RaggedFeature(tf.int64),
}
feature_tensors = tf.io.parse_example(example_batch, feature_specification)
for name, value in feature_tensors.items():
print("{}={}".format(name, value))
tf.io.RaggedFeature 也可用於讀取具有多個參差不齊維度的特徵。如需詳細資訊,請參閱 API 說明文件。
資料集
tf.data 是一種 API,可讓您從簡單、可重複使用的部分建構複雜的輸入管道。其核心資料結構是 tf.data.Dataset,代表一連串元素,其中每個元素都由一或多個元件組成。
# Helper function used to print datasets in the examples below.
def print_dictionary_dataset(dataset):
for i, element in enumerate(dataset):
print("Element {}:".format(i))
for (feature_name, feature_value) in element.items():
print('{:>14} = {}'.format(feature_name, feature_value))
使用參差不齊張量建構資料集
可以使用與從 tf.Tensor 或 NumPy array 建構資料集相同的方法,從參差不齊張量建構資料集,例如 Dataset.from_tensor_slices
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(feature_tensors)
print_dictionary_dataset(dataset)
使用參差不齊張量進行資料集批次處理和取消批次處理
具有參差不齊張量的資料集可以使用 Dataset.batch 方法進行批次處理 (將「n」個連續元素合併為單一元素)。
batched_dataset = dataset.batch(2)
print_dictionary_dataset(batched_dataset)
反之,可以使用 Dataset.unbatch 將批次資料集轉換為扁平資料集。
unbatched_dataset = batched_dataset.unbatch()
print_dictionary_dataset(unbatched_dataset)
使用可變長度非參差不齊張量進行資料集批次處理
如果您有包含非參差不齊張量的資料集,且張量長度在元素之間有所不同,則可以套用 dense_to_ragged_batch 轉換,將這些非參差不齊張量批次處理為參差不齊張量
non_ragged_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices([1, 5, 3, 2, 8])
non_ragged_dataset = non_ragged_dataset.map(tf.range)
batched_non_ragged_dataset = non_ragged_dataset.apply(
tf.data.experimental.dense_to_ragged_batch(2))
for element in batched_non_ragged_dataset:
print(element)
轉換具有參差不齊張量的資料集
您也可以使用 Dataset.map 在資料集中建立或轉換參差不齊張量
def transform_lengths(features):
return {
'mean_length': tf.math.reduce_mean(features['lengths']),
'length_ranges': tf.ragged.range(features['lengths'])}
transformed_dataset = dataset.map(transform_lengths)
print_dictionary_dataset(transformed_dataset)
tf.function
tf.function 是一個裝飾器,可為 Python 函式預先計算 TensorFlow 圖,這可以大幅提升 TensorFlow 程式碼的效能。參差不齊張量可以與 @tf.function 裝飾的函式透明地搭配使用。例如,下列函式適用於參差不齊和非參差不齊張量
@tf.function
def make_palindrome(x, axis):
return tf.concat([x, tf.reverse(x, [axis])], axis)
make_palindrome(tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]), axis=1)
make_palindrome(tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]]), axis=1)
如果您想要明確指定 tf.function 的 input_signature,則可以使用 tf.RaggedTensorSpec 執行此操作。
@tf.function(
input_signature=[tf.RaggedTensorSpec(shape=[None, None], dtype=tf.int32)])
def max_and_min(rt):
return (tf.math.reduce_max(rt, axis=-1), tf.math.reduce_min(rt, axis=-1))
max_and_min(tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]]))
具體函式
具體函式 封裝由 tf.function 建構的個別追蹤圖。參差不齊張量可以與具體函式透明地搭配使用。
@tf.function
def increment(x):
return x + 1
rt = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]])
cf = increment.get_concrete_function(rt)
print(cf(rt))
SavedModel
SavedModel 是一個序列化 TensorFlow 程式,包括權重和運算。它可以從 Keras 模型或自訂模型建構。在任一情況下,參差不齊張量都可以與 SavedModel 定義的函式和方法透明地搭配使用。
範例:儲存 Keras 模型
import tempfile
keras_module_path = tempfile.mkdtemp()
tf.saved_model.save(keras_model, keras_module_path)
imported_model = tf.saved_model.load(keras_module_path)
imported_model(hashed_words)
範例:儲存自訂模型
class CustomModule(tf.Module):
def __init__(self, variable_value):
super(CustomModule, self).__init__()
self.v = tf.Variable(variable_value)
@tf.function
def grow(self, x):
return x * self.v
module = CustomModule(100.0)
# Before saving a custom model, you must ensure that concrete functions are
# built for each input signature that you will need.
module.grow.get_concrete_function(tf.RaggedTensorSpec(shape=[None, None],
dtype=tf.float32))
custom_module_path = tempfile.mkdtemp()
tf.saved_model.save(module, custom_module_path)
imported_model = tf.saved_model.load(custom_module_path)
imported_model.grow(tf.ragged.constant([[1.0, 4.0, 3.0], [2.0]]))
多載運算子
RaggedTensor 類別多載標準 Python 算術和比較運算子,讓您能夠輕鬆執行基本元素級數學運算
x = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]])
y = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 1], [2], [3, 3, 3]])
print(x + y)
由於多載運算子會執行元素級計算,因此所有二元運算的輸入都必須具有相同的形狀,或可廣播為相同的形狀。在最簡單的廣播案例中,單一純量會與參差不齊張量中的每個值進行元素級組合
x = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(x + 3)
如需更進階案例的討論,請查看「廣播」章節。
參差不齊張量多載與一般 Tensor 相同的運算子集:一元運算子 -、~ 和 abs();以及二元運算子 +、-、*、/、//、%、**、&、|、^、==、<、<=、> 和 >=。
索引編製
參差不齊張量支援 Python 樣式的索引編製,包括多維度索引編製和切片。下列範例示範 2D 和 3D 參差不齊張量的參差不齊張量索引編製。
索引編製範例:2D 參差不齊張量
queries = tf.ragged.constant(
[['Who', 'is', 'George', 'Washington'],
['What', 'is', 'the', 'weather', 'tomorrow'],
['Goodnight']])
print(queries[1]) # A single query
print(queries[1, 2]) # A single word
print(queries[1:]) # Everything but the first row
print(queries[:, :3]) # The first 3 words of each query
print(queries[:, -2:]) # The last 2 words of each query
索引編製範例:3D 參差不齊張量
rt = tf.ragged.constant([[[1, 2, 3], [4]],
[[5], [], [6]],
[[7]],
[[8, 9], [10]]])
print(rt[1]) # Second row (2D RaggedTensor)
print(rt[3, 0]) # First element of fourth row (1D Tensor)
print(rt[:, 1:3]) # Items 1-3 of each row (3D RaggedTensor)
print(rt[:, -1:]) # Last item of each row (3D RaggedTensor)
RaggedTensor 支援多維度索引編製和切片,但有一個限制:不允許編製參差不齊維度的索引。這種情況有問題,因為指示的值可能存在於某些列中,但不存在於其他列中。在這種情況下,不明確的是您應該 (1) 引發 IndexError;(2) 使用預設值;還是 (3) 略過該值並傳回列數少於您開始時的張量。遵循 Python 的指導原則 («面對模稜兩可,拒絕臆測的誘惑»),目前不允許此運算。
張量類型轉換
RaggedTensor 類別定義可用於在 RaggedTensor 與 tf.Tensor 或 tf.SparseTensors 之間轉換的方法
ragged_sentences = tf.ragged.constant([
['Hi'], ['Welcome', 'to', 'the', 'fair'], ['Have', 'fun']])
# RaggedTensor -> Tensor
print(ragged_sentences.to_tensor(default_value='', shape=[None, 10]))
# Tensor -> RaggedTensor
x = [[1, 3, -1, -1], [2, -1, -1, -1], [4, 5, 8, 9]]
print(tf.RaggedTensor.from_tensor(x, padding=-1))
#RaggedTensor -> SparseTensor
print(ragged_sentences.to_sparse())
# SparseTensor -> RaggedTensor
st = tf.SparseTensor(indices=[[0, 0], [2, 0], [2, 1]],
values=['a', 'b', 'c'],
dense_shape=[3, 3])
print(tf.RaggedTensor.from_sparse(st))
評估參差不齊張量
若要存取參差不齊張量中的值,您可以:
- 使用
tf.RaggedTensor.to_list將參差不齊張量轉換為巢狀 Python 清單。 - 使用
tf.RaggedTensor.numpy將參差不齊張量轉換為 NumPy 陣列,其值為巢狀 NumPy 陣列。 - 使用
tf.RaggedTensor.values和tf.RaggedTensor.row_splits屬性或列分割方法 (例如tf.RaggedTensor.row_lengths和tf.RaggedTensor.value_rowids) 將參差不齊張量分解為其元件。 - 使用 Python 索引編製從參差不齊張量選取值。
rt = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6], [], [7]])
print("Python list:", rt.to_list())
print("NumPy array:", rt.numpy())
print("Values:", rt.values.numpy())
print("Splits:", rt.row_splits.numpy())
print("Indexed value:", rt[1].numpy())
參差不齊形狀
張量的形狀 (shape) 指定每個軸的大小。例如,[[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]] 的形狀是 [3, 2],因為它有 3 列和 2 欄。TensorFlow 有兩種各自獨立但相關的方式來描述形狀。
靜態形狀 (static shape):關於軸大小的資訊,此資訊為靜態已知 (例如,追蹤
tf.function時)。可能會部分指定。動態形狀 (dynamic shape):關於軸大小的執行階段資訊。
靜態形狀
張量的靜態形狀包含在圖表建構時已知的軸大小相關資訊。對於 tf.Tensor 和 tf.RaggedTensor,可以使用 .shape 屬性取得靜態形狀,並使用 tf.TensorShape 進行編碼。
x = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
x.shape # shape of a tf.tensor
rt = tf.ragged.constant([[1], [2, 3], [], [4]])
rt.shape # shape of a tf.RaggedTensor
不規則維度的靜態形狀永遠是 None (亦即,未指定)。但是,反之則不然 -- 如果 TensorShape 維度是 None,則可能表示該維度是不規則的,或者可能表示該維度是均勻的,但其大小為靜態未知。
動態形狀
張量的動態形狀包含在圖表執行時已知的軸大小相關資訊。它是使用 tf.shape 運算建構而成。對於 tf.Tensor,tf.shape 會以 1D 整數 Tensor 的形式傳回形狀,其中 tf.shape(x)[i] 是軸 i 的大小。
x = tf.constant([['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd'], ['e', 'f']])
tf.shape(x)
但是,1D Tensor 不足以描述 tf.RaggedTensor 的形狀。相反地,不規則張量的動態形狀是使用專用類型 tf.experimental.DynamicRaggedShape 進行編碼。在以下範例中,tf.shape(rt) 傳回的 DynamicRaggedShape 表示不規則張量有 4 列,長度分別為 1、3、0 和 2。
rt = tf.ragged.constant([[1], [2, 3, 4], [], [5, 6]])
rt_shape = tf.shape(rt)
print(rt_shape)
動態形狀:運算
DynamicRaggedShape 可與大多數預期形狀的 TensorFlow 運算搭配使用,包括 tf.reshape、tf.zeros、tf.ones、tf.fill、tf.broadcast_dynamic_shape 和 tf.broadcast_to。
print(f"tf.reshape(x, rt_shape) = {tf.reshape(x, rt_shape)}")
print(f"tf.zeros(rt_shape) = {tf.zeros(rt_shape)}")
print(f"tf.ones(rt_shape) = {tf.ones(rt_shape)}")
print(f"tf.fill(rt_shape, 9) = {tf.fill(rt_shape, 'x')}")
動態形狀:索引和切片
DynamicRaggedShape 也可以建立索引,以取得均勻維度的大小。例如,我們可以使用 tf.shape(rt)[0] 找出不規則張量中的列數 (就像對非不規則張量執行一樣)。
rt_shape[0]
但是,嘗試使用索引來擷取不規則維度的大小是錯誤的,因為它沒有單一大小。(由於 RaggedTensor 會追蹤哪些軸是不規則的,因此只有在立即執行或追蹤 tf.function 時才會擲回此錯誤;在執行具體函式時,永遠不會擲回此錯誤。)
try:
rt_shape[1]
except ValueError as e:
print("Got expected ValueError:", e)
DynamicRaggedShape 也可以進行切片,只要切片以軸 0 開頭,或僅包含密集維度即可。
rt_shape[:1]
動態形狀:編碼
DynamicRaggedShape 是使用兩個欄位進行編碼。
inner_shape:一個整數向量,提供密集tf.Tensor的形狀。row_partitions:tf.experimental.RowPartition物件的清單,說明應如何分割內部形狀的最外層維度以新增不規則軸。
如需關於列分割的詳細資訊,請參閱下方的「不規則張量編碼」一節,以及 tf.experimental.RowPartition 的 API 文件。
動態形狀:建構
DynamicRaggedShape 最常透過將 tf.shape 套用至 RaggedTensor 來建構,但也可以直接建構。
tf.experimental.DynamicRaggedShape(
row_partitions=[tf.experimental.RowPartition.from_row_lengths([5, 3, 2])],
inner_shape=[10, 8])
如果所有列的長度為靜態已知,則也可以使用 DynamicRaggedShape.from_lengths 建構動態不規則形狀。(這主要適用於測試和示範程式碼,因為不規則維度的長度很少是靜態已知的)。
tf.experimental.DynamicRaggedShape.from_lengths([4, (2, 1, 0, 8), 12])
廣播
廣播是使具有不同形狀的張量具有相容形狀以進行逐元素運算的程序。如需關於廣播的更多背景資訊,請參閱:
將兩個輸入 x 和 y 廣播為具有相容形狀的基本步驟如下:
如果
x和y的維度數量不同,則新增外部維度 (大小為 1),直到它們的維度數量相同為止。針對
x和y具有不同大小的每個維度:
- 如果
x或y在維度d中的大小為1,則在維度d中重複其值,以符合另一個輸入的大小。 - 否則,擲回例外狀況 (
x和y不具備廣播相容性)。
其中,均勻維度中張量的大小是單一數字 (跨該維度的切片大小);而不規則維度中張量的大小是切片長度的清單 (適用於跨該維度的所有切片)。
廣播範例
# x (2D ragged): 2 x (num_rows)
# y (scalar)
# result (2D ragged): 2 x (num_rows)
x = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3]])
y = 3
print(x + y)
# x (2d ragged): 3 x (num_rows)
# y (2d tensor): 3 x 1
# Result (2d ragged): 3 x (num_rows)
x = tf.ragged.constant(
[[10, 87, 12],
[19, 53],
[12, 32]])
y = [[1000], [2000], [3000]]
print(x + y)
# x (3d ragged): 2 x (r1) x 2
# y (2d ragged): 1 x 1
# Result (3d ragged): 2 x (r1) x 2
x = tf.ragged.constant(
[[[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]],
[[7, 8]]],
ragged_rank=1)
y = tf.constant([[10]])
print(x + y)
# x (3d ragged): 2 x (r1) x (r2) x 1
# y (1d tensor): 3
# Result (3d ragged): 2 x (r1) x (r2) x 3
x = tf.ragged.constant(
[
[
[[1], [2]],
[],
[[3]],
[[4]],
],
[
[[5], [6]],
[[7]]
]
],
ragged_rank=2)
y = tf.constant([10, 20, 30])
print(x + y)
以下是一些不廣播的形狀範例:
# x (2d ragged): 3 x (r1)
# y (2d tensor): 3 x 4 # trailing dimensions do not match
x = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4, 5, 6], [7]])
y = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]])
try:
x + y
except tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError as exception:
print(exception)
# x (2d ragged): 3 x (r1)
# y (2d ragged): 3 x (r2) # ragged dimensions do not match.
x = tf.ragged.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4], [5, 6]])
y = tf.ragged.constant([[10, 20], [30, 40], [50]])
try:
x + y
except tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError as exception:
print(exception)
# x (3d ragged): 3 x (r1) x 2
# y (3d ragged): 3 x (r1) x 3 # trailing dimensions do not match
x = tf.ragged.constant([[[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]],
[[7, 8], [9, 10]]])
y = tf.ragged.constant([[[1, 2, 0], [3, 4, 0], [5, 6, 0]],
[[7, 8, 0], [9, 10, 0]]])
try:
x + y
except tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError as exception:
print(exception)
不規則張量編碼
不規則張量是使用 RaggedTensor 類別進行編碼。在內部,每個 RaggedTensor 都包含:
- 一個
values張量,它會將變長列串連成扁平化清單。 - 一個
row_partition,它會指示如何將這些扁平化值分成列。
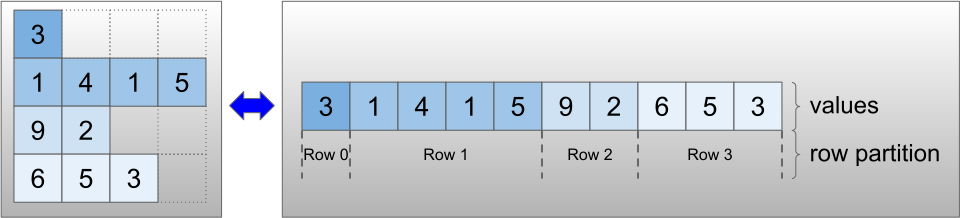
row_partition 可以使用四種不同的編碼方式儲存:
row_splits是一個整數向量,用於指定列之間的分裂點。value_rowids是一個整數向量,用於指定每個值的列索引。row_lengths是一個整數向量,用於指定每列的長度。uniform_row_length是一個整數純量,用於指定所有列的單一長度。
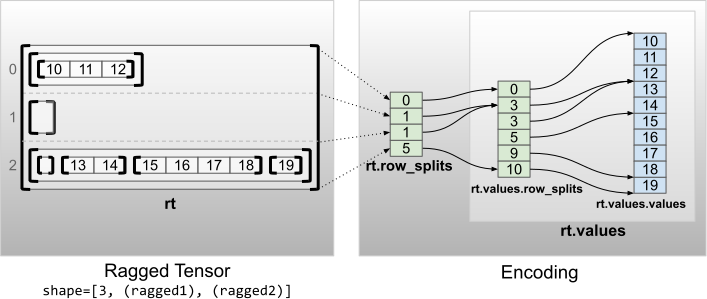
整數純量 nrows 也可以包含在 row_partition 編碼中,以考量具有 value_rowids 的空白結尾列,或具有 uniform_row_length 的空白列。
rt = tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(
values=[3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2],
row_splits=[0, 4, 4, 6, 7])
print(rt)
列分割要使用哪種編碼方式的選擇,是由不規則張量在內部管理,以提升某些情境中的效率。特別是,不同列分割配置的一些優點和缺點如下:
- 有效率的索引:
row_splits編碼能夠對不規則張量進行常數時間索引和切片。 - 有效率的串連:在串連不規則張量時,
row_lengths編碼更有效率,因為當兩個張量串連在一起時,列長度不會變更。 - 編碼大小較小:當儲存具有大量空白列的不規則張量時,
value_rowids編碼更有效率,因為張量的大小僅取決於值的總數。另一方面,當儲存具有較長列的不規則張量時,row_splits和row_lengths編碼更有效率,因為它們每列只需要一個純量值。 - 相容性:
value_rowids配置符合 分段 作業 (例如tf.segment_sum) 使用的格式。row_limits配置符合作業 (例如tf.sequence_mask) 使用的格式。 - 均勻維度:如下所述,
uniform_row_length編碼用於編碼具有均勻維度的不規則張量。
多個不規則維度
具有多個不規則維度的不規則張量,是透過對 values 張量使用巢狀 RaggedTensor 進行編碼。每個巢狀 RaggedTensor 都會新增單一不規則維度。
rt = tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(
values=tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(
values=[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
row_splits=[0, 3, 3, 5, 9, 10]),
row_splits=[0, 1, 1, 5])
print(rt)
print("Shape: {}".format(rt.shape))
print("Number of partitioned dimensions: {}".format(rt.ragged_rank))
工廠函式 tf.RaggedTensor.from_nested_row_splits 可用於直接建構具有多個不規則維度的 RaggedTensor,方法是提供 row_splits 張量的清單。
rt = tf.RaggedTensor.from_nested_row_splits(
flat_values=[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
nested_row_splits=([0, 1, 1, 5], [0, 3, 3, 5, 9, 10]))
print(rt)
不規則階數和扁平化值
不規則張量的不規則階數 (ragged rank) 是底層 values 張量已分割的次數 (亦即 RaggedTensor 物件的巢狀深度)。最內層的 values 張量稱為其flat_values。在以下範例中,conversations 的 ragged_rank=3,而其 flat_values 是具有 24 個字串的 1D Tensor。
# shape = [batch, (paragraph), (sentence), (word)]
conversations = tf.ragged.constant(
[[[["I", "like", "ragged", "tensors."]],
[["Oh", "yeah?"], ["What", "can", "you", "use", "them", "for?"]],
[["Processing", "variable", "length", "data!"]]],
[[["I", "like", "cheese."], ["Do", "you?"]],
[["Yes."], ["I", "do."]]]])
conversations.shape
assert conversations.ragged_rank == len(conversations.nested_row_splits)
conversations.ragged_rank # Number of partitioned dimensions.
conversations.flat_values.numpy()
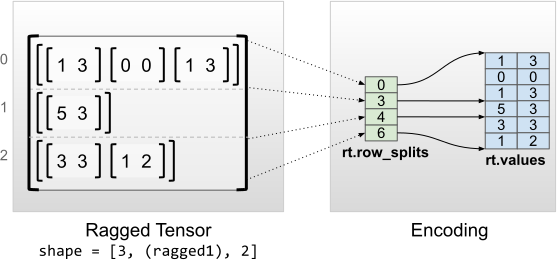
均勻內部維度
具有均勻內部維度的不規則張量,是透過對 flat_values (亦即最內層的 values) 使用多維 tf.Tensor 進行編碼。
rt = tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(
values=[[1, 3], [0, 0], [1, 3], [5, 3], [3, 3], [1, 2]],
row_splits=[0, 3, 4, 6])
print(rt)
print("Shape: {}".format(rt.shape))
print("Number of partitioned dimensions: {}".format(rt.ragged_rank))
print("Flat values shape: {}".format(rt.flat_values.shape))
print("Flat values:\n{}".format(rt.flat_values))
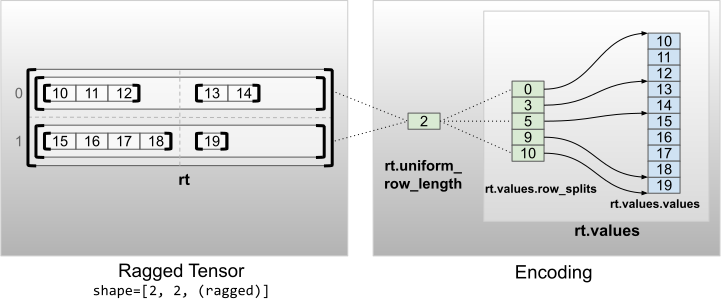
均勻非內部維度
具有均勻非內部維度的不規則張量,是透過使用 uniform_row_length 分割列進行編碼。
rt = tf.RaggedTensor.from_uniform_row_length(
values=tf.RaggedTensor.from_row_splits(
values=[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
row_splits=[0, 3, 5, 9, 10]),
uniform_row_length=2)
print(rt)
print("Shape: {}".format(rt.shape))
print("Number of partitioned dimensions: {}".format(rt.ragged_rank))
