 在 TensorFlow.org 上檢視 在 TensorFlow.org 上檢視
|
 在 Google Colab 中執行 在 Google Colab 中執行
|
 在 GitHub 上檢視原始碼 在 GitHub 上檢視原始碼
|
 下載筆記本 下載筆記本
|
總覽
「tf.distribute.Strategy」API 提供抽象化功能,可將訓練作業分散至多個處理單元。您可以使用現有的模型和訓練程式碼進行分散式訓練,只需進行極少的變更。
本教學課程示範如何使用「tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy」,透過單一機器上多個 GPU 的同步訓練來執行圖內複製。此策略基本上會將模型的所有變數複製到每個處理器。接著,它會使用 all-reduce 結合來自所有處理器的梯度,並將結合後的值套用至模型的所有副本。
您將使用 tf.keras API 建構模型,並使用 Model.fit 進行訓練。(如要瞭解如何透過自訂訓練迴圈和 MirroredStrategy 進行分散式訓練,請參閱本教學課程。)
MirroredStrategy 會在單一機器上的多個 GPU 上訓練模型。如要進行多部機器上多個 GPU 的同步訓練,請搭配 tf.distribute.MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy 和 Keras Model.fit 或 自訂訓練迴圈。如需其他選項,請參閱分散式訓練指南。
如要瞭解其他各種策略,請參閱TensorFlow 分散式訓練指南。
設定
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
import tensorflow as tf
import os
# Load the TensorBoard notebook extension.
%load_ext tensorboard
print(tf.__version__)
下載資料集
從TensorFlow Datasets 載入 MNIST 資料集。這會傳回 tf.data 格式的資料集。
將 with_info 引數設為 True 會納入整個資料集的metadata,並儲存至此處的 info。除其他項目外,這個metadata物件還包含訓練和測試範例的數量。
datasets, info = tfds.load(name='mnist', with_info=True, as_supervised=True)
mnist_train, mnist_test = datasets['train'], datasets['test']
定義分散策略
建立 MirroredStrategy 物件。這會處理分散作業,並提供內容管理員 (MirroredStrategy.scope) 以在其中建構模型。
strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()
print('Number of devices: {}'.format(strategy.num_replicas_in_sync))
設定輸入管線
使用多個 GPU 訓練模型時,您可以增加批次大小,有效運用額外的運算能力。一般來說,請使用符合 GPU 記憶體容量的最大批次大小,並據此調整學習率。
# You can also do info.splits.total_num_examples to get the total
# number of examples in the dataset.
num_train_examples = info.splits['train'].num_examples
num_test_examples = info.splits['test'].num_examples
BUFFER_SIZE = 10000
BATCH_SIZE_PER_REPLICA = 64
BATCH_SIZE = BATCH_SIZE_PER_REPLICA * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
定義一個函式,將圖片像素值從 [0, 255] 範圍標準化為 [0, 1] 範圍 (特徵縮放)
def scale(image, label):
image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32)
image /= 255
return image, label
將這個 scale 函式套用至訓練和測試資料,然後使用 tf.data.Dataset API 隨機處理訓練資料 (Dataset.shuffle) 並將其分批 (Dataset.batch)。請注意,您也會將訓練資料的記憶體內快取保留下來,以提升效能 (Dataset.cache)。
train_dataset = mnist_train.map(scale).cache().shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
eval_dataset = mnist_test.map(scale).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
建立模型並例項化最佳化工具
在 Strategy.scope 的環境定義中,使用 Keras API 建立並編譯模型
with strategy.scope():
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)
])
model.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
metrics=['accuracy'])
在這個使用 MNIST 資料集的玩具範例中,您將使用 Adam 最佳化工具的預設學習率 0.001。
對於較大的資料集,分散式訓練的主要優點是在每個訓練步驟中學習更多,因為每個步驟都會平行處理更多訓練資料,進而允許使用較大的學習率 (在模型和資料集的限制範圍內)。
定義回呼
定義下列 Keras 回呼
tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard:為 TensorBoard 寫入記錄,讓您可以視覺化圖表。tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint:以特定頻率儲存模型,例如在每個 epoch 之後。tf.keras.callbacks.BackupAndRestore:透過備份模型和目前的 epoch 號碼,提供容錯功能。如要瞭解詳情,請參閱搭配 Keras 進行多 worker 訓練教學課程中的「容錯」章節。tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler:排定學習率變更時程,例如在每個 epoch/批次之後。
為了說明用途,請新增名為 PrintLR 的自訂回呼,以在筆記本中顯示學習率。
# Define the checkpoint directory to store the checkpoints.
checkpoint_dir = './training_checkpoints'
# Define the name of the checkpoint files.
checkpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, "ckpt_{epoch}")
# Define a function for decaying the learning rate.
# You can define any decay function you need.
def decay(epoch):
if epoch < 3:
return 1e-3
elif epoch >= 3 and epoch < 7:
return 1e-4
else:
return 1e-5
# Define a callback for printing the learning rate at the end of each epoch.
class PrintLR(tf.keras.callbacks.Callback):
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs=None):
print('\nLearning rate for epoch {} is {}'.format( epoch + 1, model.optimizer.lr.numpy()))
# Put all the callbacks together.
callbacks = [
tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir='./logs'),
tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_prefix,
save_weights_only=True),
tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(decay),
PrintLR()
]
訓練與評估
現在,以一般方式訓練模型,方法是在模型上呼叫 Keras Model.fit,並傳入在本教學課程開頭建立的資料集。無論您是否要分散訓練作業,這個步驟都相同。
EPOCHS = 12
model.fit(train_dataset, epochs=EPOCHS, callbacks=callbacks)
檢查已儲存的檢查點
# Check the checkpoint directory.ls {checkpoint_dir}
如要檢查模型效能,請載入最新的檢查點,並在測試資料上呼叫 Model.evaluate
model.load_weights(tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir))
eval_loss, eval_acc = model.evaluate(eval_dataset)
print('Eval loss: {}, Eval accuracy: {}'.format(eval_loss, eval_acc))
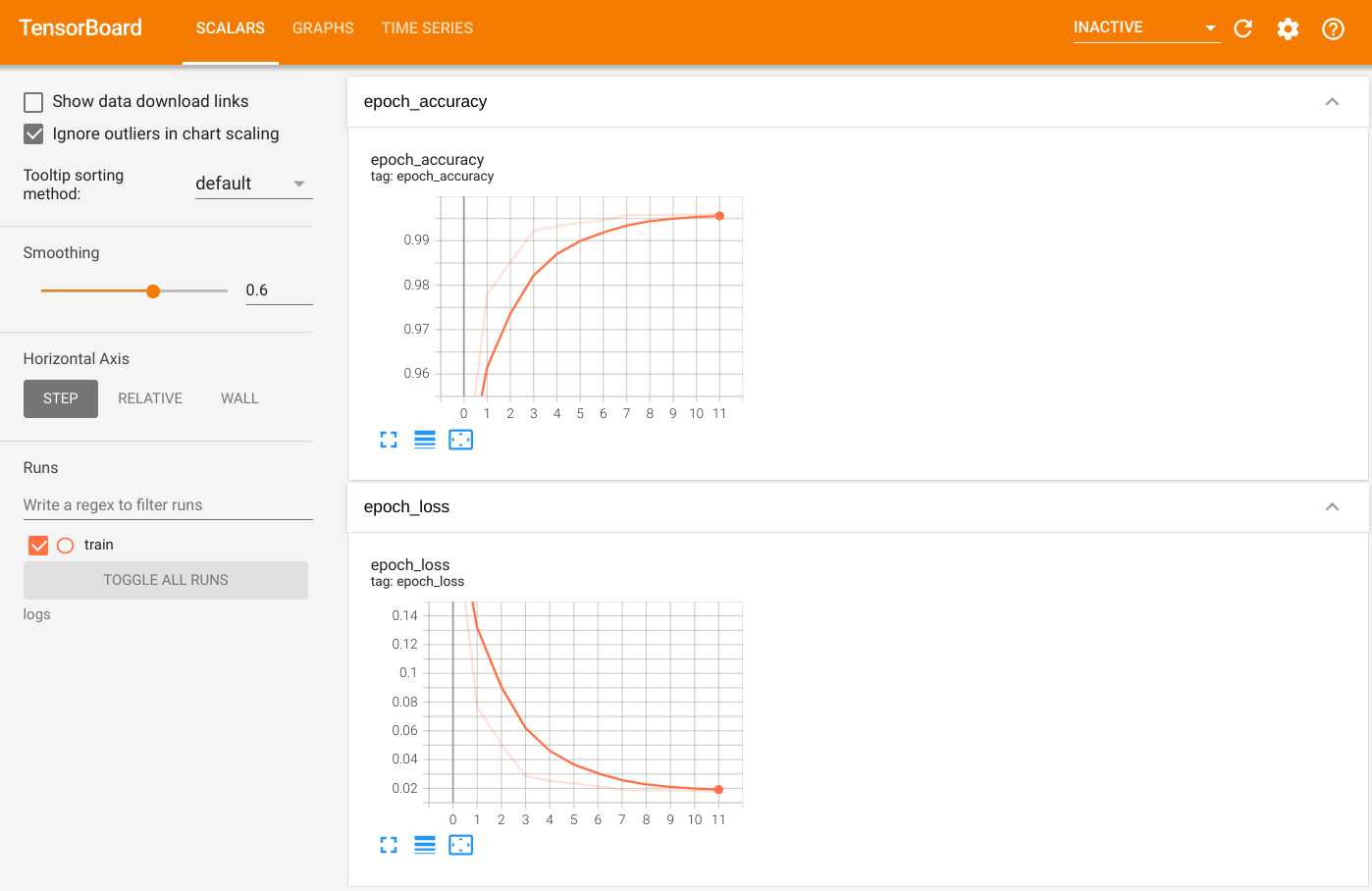
如要視覺化輸出內容,請啟動 TensorBoard 並檢視記錄。
%tensorboard --logdir=logs
ls -sh ./logs
儲存模型
使用 Model.save 將模型儲存至 .keras zip 封存檔。模型儲存完畢後,您可以選擇是否使用 Strategy.scope 來載入模型。
path = 'my_model.keras'
model.save(path)
現在,在不使用 Strategy.scope 的情況下載入模型
unreplicated_model = tf.keras.models.load_model(path)
unreplicated_model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
eval_loss, eval_acc = unreplicated_model.evaluate(eval_dataset)
print('Eval loss: {}, Eval Accuracy: {}'.format(eval_loss, eval_acc))
在使用 Strategy.scope 的情況下載入模型
with strategy.scope():
replicated_model = tf.keras.models.load_model(path)
replicated_model.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
eval_loss, eval_acc = replicated_model.evaluate(eval_dataset)
print ('Eval loss: {}, Eval Accuracy: {}'.format(eval_loss, eval_acc))
其他資源
更多範例,示範如何搭配 Keras Model.fit API 使用不同的分散策略
- 使用 BERT 在 TPU 上解決 GLUE 任務教學課程使用
tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy在 GPU 上進行訓練,並使用tf.distribute.TPUStrategy在 TPU 上進行訓練。 - 使用分散策略儲存及載入模型教學課程示範如何搭配
tf.distribute.Strategy使用 SavedModel API。 - 官方 TensorFlow 模型可設定為執行多種分散策略。
如要進一步瞭解 TensorFlow 分散策略
- 透過 tf.distribute.Strategy 進行自訂訓練教學課程說明如何搭配自訂訓練迴圈使用
tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy進行單一 worker 訓練。 - 搭配 Keras 進行多 worker 訓練教學課程說明如何搭配
Model.fit使用MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy。 - 搭配 Keras 和 MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy 進行自訂訓練迴圈教學課程說明如何搭配 Keras 和自訂訓練迴圈使用
MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy。 - TensorFlow 分散式訓練指南概述可用的分散策略。
- 使用 tf.function 提升效能指南提供其他策略和工具的相關資訊,例如您可以用來最佳化 TensorFlow 模型效能的 TensorFlow Profiler。
