 在 TensorFlow.org 上檢視 在 TensorFlow.org 上檢視
|
 在 Google Colab 中執行 在 Google Colab 中執行
|
 在 GitHub 上檢視 在 GitHub 上檢視
|
 下載筆記本 下載筆記本
|
 查看 TF Hub 模型 查看 TF Hub 模型
|
這個 Colab 將示範如何使用從 TensorFlow Hub 下載的 SPICE 模型。
sudo apt-get install -q -y timidity libsndfile1
Reading package lists... Building dependency tree... Reading state information... libsndfile1 is already the newest version (1.0.28-7ubuntu0.2). The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required: libatasmart4 libblockdev-fs2 libblockdev-loop2 libblockdev-part-err2 libblockdev-part2 libblockdev-swap2 libblockdev-utils2 libblockdev2 libparted-fs-resize0 libxmlb2 Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them. The following additional packages will be installed: fluid-soundfont-gm libao-common libao4 Suggested packages: fluid-soundfont-gs fluidsynth libaudio2 libsndio6.1 freepats pmidi timidity-daemon The following NEW packages will be installed: fluid-soundfont-gm libao-common libao4 timidity 0 upgraded, 4 newly installed, 0 to remove and 188 not upgraded. Need to get 120 MB of archives. After this operation, 150 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 fluid-soundfont-gm all 3.1-5.1 [119 MB] Get:2 http://us-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/main amd64 libao-common all 1.2.2+20180113-1ubuntu1 [6644 B] Get:3 http://us-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/main amd64 libao4 amd64 1.2.2+20180113-1ubuntu1 [35.1 kB] Get:4 http://us-east1.gce.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/universe amd64 timidity amd64 2.14.0-8build1 [613 kB] Fetched 120 MB in 2s (64.8 MB/s) Selecting previously unselected package fluid-soundfont-gm. (Reading database ... 144021 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../fluid-soundfont-gm_3.1-5.1_all.deb ... Unpacking fluid-soundfont-gm (3.1-5.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libao-common. Preparing to unpack .../libao-common_1.2.2+20180113-1ubuntu1_all.deb ... Unpacking libao-common (1.2.2+20180113-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libao4:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../libao4_1.2.2+20180113-1ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libao4:amd64 (1.2.2+20180113-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package timidity. Preparing to unpack .../timidity_2.14.0-8build1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking timidity (2.14.0-8build1) ... Setting up libao-common (1.2.2+20180113-1ubuntu1) ... Setting up libao4:amd64 (1.2.2+20180113-1ubuntu1) ... Setting up fluid-soundfont-gm (3.1-5.1) ... Setting up timidity (2.14.0-8build1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.31-0ubuntu9.12) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.1-1) ... Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.24-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for mime-support (3.64ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.36.0-1ubuntu1) ...
# All the imports to deal with sound datapip install pydub librosa music21
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import librosa
from librosa import display as librosadisplay
import logging
import math
import statistics
import sys
from IPython.display import Audio, Javascript
from scipy.io import wavfile
from base64 import b64decode
import music21
from pydub import AudioSegment
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.ERROR)
print("tensorflow: %s" % tf.__version__)
#print("librosa: %s" % librosa.__version__)
tensorflow: 2.16.1
音訊輸入檔案
現在是最困難的部分:錄下您的歌聲!:)
我們提供四種方法來取得音訊檔案
- 直接在 Colab 中錄製音訊
- 從您的電腦上傳
- 使用儲存在 Google 雲端硬碟上的檔案
- 從網路上下載檔案
從以下四種方法中選擇一種。
[執行此程式碼] 從瀏覽器直接錄製音訊的 JS 程式碼定義
選取如何輸入您的音訊
You selected https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/c-scale-metronome.wav --2024-03-09 13:03:30-- https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/c-scale-metronome.wav Resolving storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)... 173.194.210.207, 173.194.218.207, 142.251.162.207, ... Connecting to storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)|173.194.210.207|:443... connected. HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK Length: 384728 (376K) [audio/wav] Saving to: ‘c-scale.wav’ c-scale.wav 100%[===================>] 375.71K --.-KB/s in 0.004s 2024-03-09 13:03:30 (92.7 MB/s) - ‘c-scale.wav’ saved [384728/384728]
準備音訊資料
現在我們有了音訊,讓我們將其轉換為預期的格式,然後聆聽!
SPICE 模型需要取樣率為 16kHz 且僅有一個聲道 (單聲道) 的音訊檔案作為輸入。
為了協助您完成這部分,我們建立了一個函式 (convert_audio_for_model),可將您擁有的任何 wav 檔案轉換為模型預期的格式
# Function that converts the user-created audio to the format that the model
# expects: bitrate 16kHz and only one channel (mono).
EXPECTED_SAMPLE_RATE = 16000
def convert_audio_for_model(user_file, output_file='converted_audio_file.wav'):
audio = AudioSegment.from_file(user_file)
audio = audio.set_frame_rate(EXPECTED_SAMPLE_RATE).set_channels(1)
audio.export(output_file, format="wav")
return output_file
# Converting to the expected format for the model
# in all the input 4 input method before, the uploaded file name is at
# the variable uploaded_file_name
converted_audio_file = convert_audio_for_model(uploaded_file_name)
# Loading audio samples from the wav file:
sample_rate, audio_samples = wavfile.read(converted_audio_file, 'rb')
# Show some basic information about the audio.
duration = len(audio_samples)/sample_rate
print(f'Sample rate: {sample_rate} Hz')
print(f'Total duration: {duration:.2f}s')
print(f'Size of the input: {len(audio_samples)}')
# Let's listen to the wav file.
Audio(audio_samples, rate=sample_rate)
Sample rate: 16000 Hz Total duration: 11.89s Size of the input: 190316
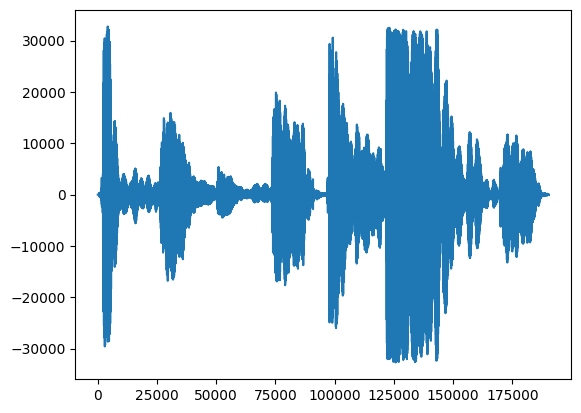
首先,讓我們看看我們歌聲的波形。
# We can visualize the audio as a waveform.
_ = plt.plot(audio_samples)
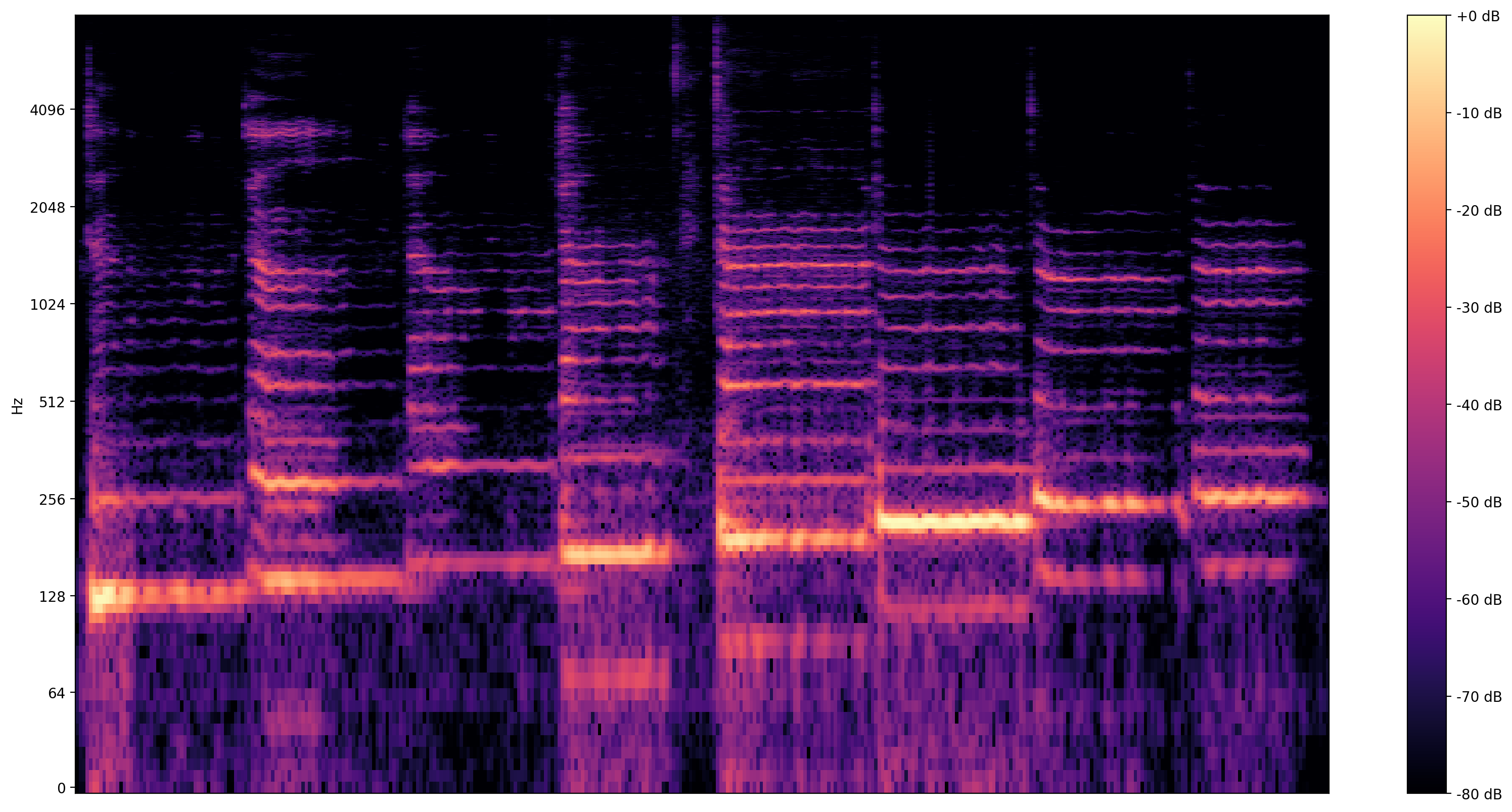
更具資訊性的視覺化是頻譜圖,它顯示了隨時間變化的頻率。
在這裡,我們使用對數頻率刻度,使歌聲更清晰可見。
MAX_ABS_INT16 = 32768.0
def plot_stft(x, sample_rate, show_black_and_white=False):
x_stft = np.abs(librosa.stft(x, n_fft=2048))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(20, 10)
x_stft_db = librosa.amplitude_to_db(x_stft, ref=np.max)
if(show_black_and_white):
librosadisplay.specshow(data=x_stft_db, y_axis='log',
sr=sample_rate, cmap='gray_r')
else:
librosadisplay.specshow(data=x_stft_db, y_axis='log', sr=sample_rate)
plt.colorbar(format='%+2.0f dB')
plot_stft(audio_samples / MAX_ABS_INT16 , sample_rate=EXPECTED_SAMPLE_RATE)
plt.show()
我們在這裡需要最後一次轉換。音訊樣本採用 int16 格式。它們需要標準化為 -1 到 1 之間的浮點數。
audio_samples = audio_samples / float(MAX_ABS_INT16)
執行模型
現在是簡單的部分,讓我們使用 TensorFlow Hub 載入模型,並將音訊饋送給它。SPICE 將為我們提供兩個輸出:音高和不確定性
TensorFlow Hub 是一個用於發布、探索和使用機器學習模型可重複使用部分的程式庫。它讓機器學習變得容易,以解決您的挑戰。
若要載入模型,您只需要 Hub 模組和指向模型的 URL
# Loading the SPICE model is easy:
model = hub.load("https://tfhub.dev/google/spice/2")
WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). 2024-03-09 13:03:40.741729: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_driver.cc:282] failed call to cuInit: CUDA_ERROR_NO_DEVICE: no CUDA-capable device is detected WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'global_step:0' shape=() dtype=int64_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/conv2d/kernel:0' shape=(1, 3, 1, 64) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/gamma:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/beta:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables(). WARNING:tensorflow:Unable to create a python object for variable <tf.Variable 'encoder/batch_normalization/moving_mean:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref> because it is a reference variable. It may not be visible to training APIs. If this is a problem, consider rebuilding the SavedModel after running tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables().
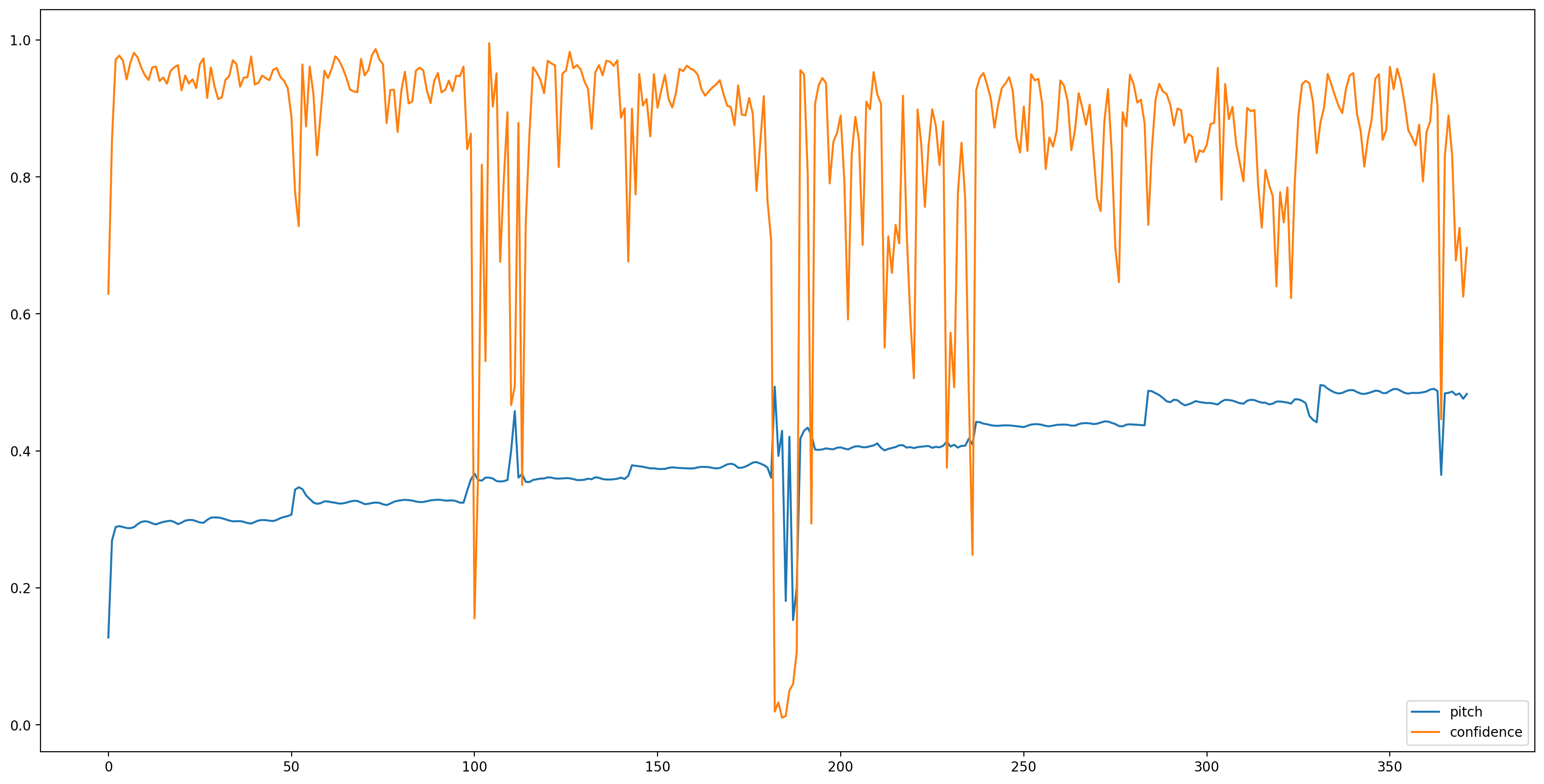
載入模型、準備好資料後,我們需要 3 行程式碼才能獲得結果
# We now feed the audio to the SPICE tf.hub model to obtain pitch and uncertainty outputs as tensors.
model_output = model.signatures["serving_default"](tf.constant(audio_samples, tf.float32))
pitch_outputs = model_output["pitch"]
uncertainty_outputs = model_output["uncertainty"]
# 'Uncertainty' basically means the inverse of confidence.
confidence_outputs = 1.0 - uncertainty_outputs
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(20, 10)
plt.plot(pitch_outputs, label='pitch')
plt.plot(confidence_outputs, label='confidence')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
讓我們透過移除所有低信賴度 (信賴度 < 0.9) 的音高估計值,並繪製剩餘的估計值,讓結果更容易理解。
confidence_outputs = list(confidence_outputs)
pitch_outputs = [ float(x) for x in pitch_outputs]
indices = range(len (pitch_outputs))
confident_pitch_outputs = [ (i,p)
for i, p, c in zip(indices, pitch_outputs, confidence_outputs) if c >= 0.9 ]
confident_pitch_outputs_x, confident_pitch_outputs_y = zip(*confident_pitch_outputs)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(20, 10)
ax.set_ylim([0, 1])
plt.scatter(confident_pitch_outputs_x, confident_pitch_outputs_y, )
plt.scatter(confident_pitch_outputs_x, confident_pitch_outputs_y, c="r")
plt.show()
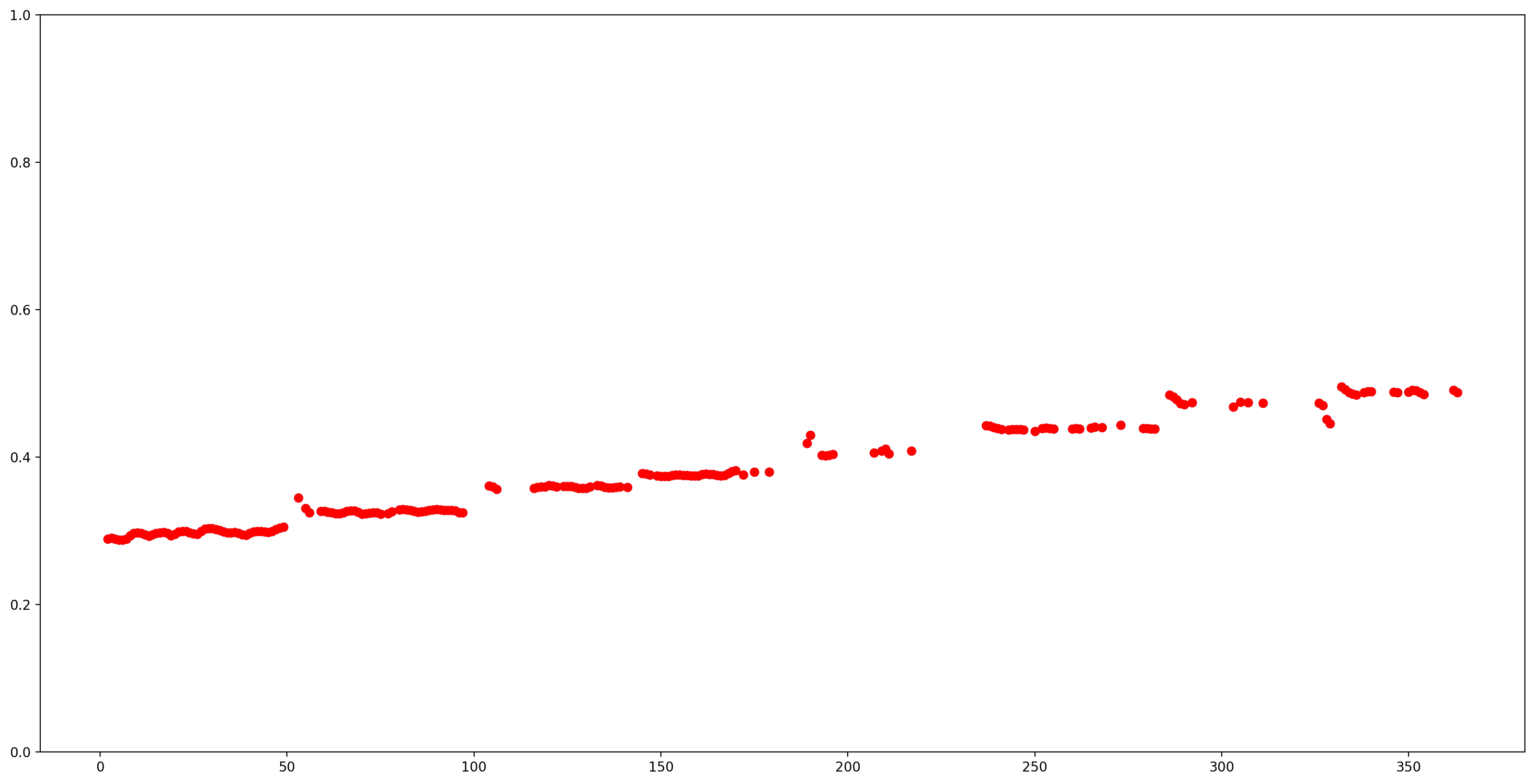
SPICE 傳回的音高值範圍為 0 到 1。讓我們將它們轉換為 Hz 的絕對音高值。
def output2hz(pitch_output):
# Constants taken from https://tfhub.dev/google/spice/2
PT_OFFSET = 25.58
PT_SLOPE = 63.07
FMIN = 10.0;
BINS_PER_OCTAVE = 12.0;
cqt_bin = pitch_output * PT_SLOPE + PT_OFFSET;
return FMIN * 2.0 ** (1.0 * cqt_bin / BINS_PER_OCTAVE)
confident_pitch_values_hz = [ output2hz(p) for p in confident_pitch_outputs_y ]
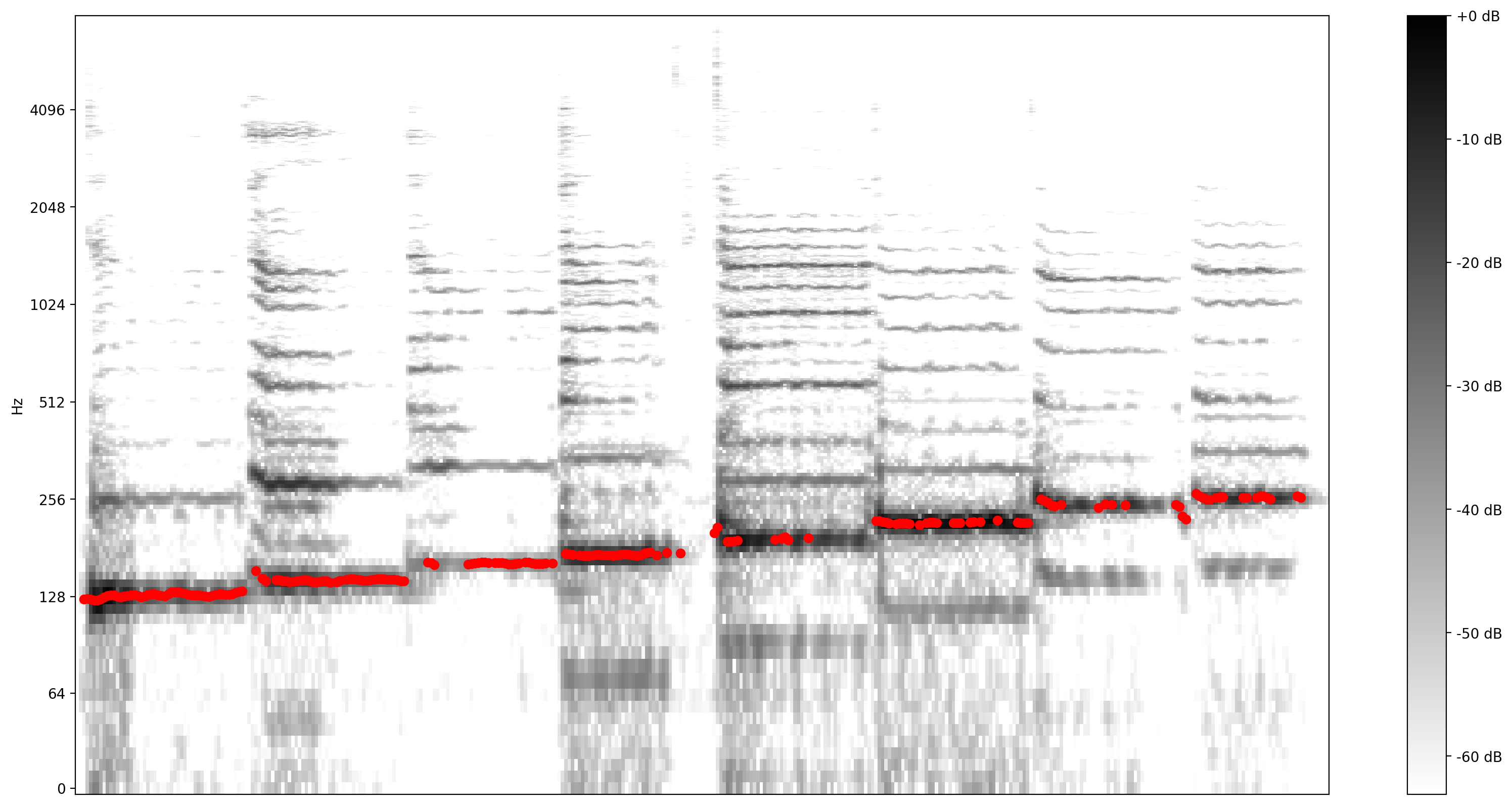
現在,讓我們看看預測效果如何:我們將預測的音高疊加在原始頻譜圖上。為了讓音高預測更明顯,我們將頻譜圖更改為黑白。
plot_stft(audio_samples / MAX_ABS_INT16 ,
sample_rate=EXPECTED_SAMPLE_RATE, show_black_and_white=True)
# Note: conveniently, since the plot is in log scale, the pitch outputs
# also get converted to the log scale automatically by matplotlib.
plt.scatter(confident_pitch_outputs_x, confident_pitch_values_hz, c="r")
plt.show()
轉換為音符
現在我們有了音高值,讓我們將它們轉換為音符!這部分本身就具有挑戰性。我們必須考慮兩件事
- 休止符 (沒有歌聲時)
- 每個音符的大小 (偏移)
1:在輸出中新增零以指示何時沒有歌聲
pitch_outputs_and_rests = [
output2hz(p) if c >= 0.9 else 0
for i, p, c in zip(indices, pitch_outputs, confidence_outputs)
]
2:新增音符偏移
當一個人自由唱歌時,旋律可能與音符可以表示的絕對音高值存在偏移。因此,為了將預測轉換為音符,需要校正這種可能的偏移。這就是以下程式碼的計算內容。
A4 = 440
C0 = A4 * pow(2, -4.75)
note_names = ["C", "C#", "D", "D#", "E", "F", "F#", "G", "G#", "A", "A#", "B"]
def hz2offset(freq):
# This measures the quantization error for a single note.
if freq == 0: # Rests always have zero error.
return None
# Quantized note.
h = round(12 * math.log2(freq / C0))
return 12 * math.log2(freq / C0) - h
# The ideal offset is the mean quantization error for all the notes
# (excluding rests):
offsets = [hz2offset(p) for p in pitch_outputs_and_rests if p != 0]
print("offsets: ", offsets)
ideal_offset = statistics.mean(offsets)
print("ideal offset: ", ideal_offset)
offsets: [0.2851094503825351, 0.3700368844097355, 0.2861639241998972, 0.19609005646164235, 0.17851737247163868, 0.2733467103665532, -0.4475297470266071, -0.24651809109990808, -0.1796576844031108, -0.23060136331860548, -0.37825965149943386, -0.4725100625926686, -0.345721333759478, -0.2436666886383776, -0.1818925674134988, -0.1348077739650435, -0.24551624699179797, -0.4454884661609313, -0.31267739488426827, -0.12241723670307181, -0.06614479972665066, -0.0670244677240106, -0.1744135098034576, -0.29365739389006507, -0.32520890458170726, -0.056438377636119696, 0.1470506338899895, 0.17167006002122775, 0.16529246704037348, 0.09569531546290477, -0.0063254962736891684, -0.11799822075907684, -0.18834910495822044, -0.17934754504506145, -0.17215419157092526, -0.23695828034226452, -0.34594501002376177, -0.39380233241860907, -0.2528674895936689, -0.11009436621014146, -0.07118597401920113, -0.08042436762396932, -0.12799786551538972, -0.16227484329287023, -0.059323613482156645, 0.10667800800259641, 0.21044687793906292, 0.2931939382975841, -0.22329278631751492, -0.12365553720538713, -0.4571117360765271, -0.34864378495755943, -0.35947798653189267, -0.4313212989145896, -0.4818984494978622, 0.44220950977261, 0.45883109973128455, -0.47095522924010425, -0.3674476282173771, -0.3047205333287053, -0.310763551729373, -0.4501382996017185, 0.396607746345353, 0.4238116671269694, 0.4982695482795947, -0.45931842459980743, -0.4890504510576079, 0.3836871527260044, 0.4441304941600137, -0.38787547393386745, -0.24855899466817277, -0.20666198684519088, -0.23811575664822726, -0.2760223047310504, -0.3641733084494305, -0.41670903606955534, -0.41009085013215696, -0.3340427999073796, -0.26122959716860805, -0.2232610212141708, -0.19940472586695535, -0.22528914465252825, -0.2780899004513415, -0.2744452930862167, -0.25655119194333764, -0.33068013741318936, -0.4678933079416083, -0.4695116715008396, -0.1648191110665067, -0.24618840082233362, -0.48052594049518405, -0.3771762286001845, -0.32261801643912236, -0.25560347987954657, -0.24629929913823645, -0.14035005553309787, -0.16659160448853783, -0.2442749349648139, -0.236978201704666, -0.20882694615665542, -0.22637519492452896, -0.29836135937516417, -0.39081484182421633, -0.3909915272766753, -0.3650074879700469, -0.26423099293057106, -0.13023387356345495, -0.18214744283501716, -0.3020830316716854, -0.33754229827467697, -0.34391613199059634, -0.3145431153351481, -0.26713502510135356, -0.2910439501578139, -0.11686573876684037, -0.1673113150770007, -0.24345522655789864, -0.30852810277288256, -0.35647376789395935, -0.37154654069487236, -0.3600168751055435, -0.2667062802488047, -0.21902000440899627, -0.2484456507736823, -0.2774126668149748, -0.2941451550895522, -0.31118966235463574, -0.32662520422285013, -0.3053966350728743, -0.2160201109821145, -0.17343891693894875, -0.17792559965198507, -0.19880831642691987, -0.2725049464279863, -0.3152139554793152, -0.28217001660411256, -0.11594847812001063, 0.0541902144377957, 0.11488166735824024, -0.2559716991955412, 0.019302356106599916, -0.002236352401425279, 0.4468796487277231, 0.15514772014076073, 0.420767605764226, 0.3854436726992816, 0.4373497234409669, -0.4694994504625001, -0.3662737943107359, -0.2035370944315602, -0.015041911142510855, -0.4185651697093675, -0.17896841837708877, -0.032896162706066434, -0.06109628869835859, -0.1953753529364306, -0.2545161090666568, -0.3363722236329778, -0.39191348357741873, -0.36531668408458984, -0.34896764083450194, -0.35455014927928374, -0.38925192399566555, 0.48781447337324835, -0.2820884378129733, -0.241937608557393, -0.24987529649083484, -0.3034899331504519, -0.29106932176892997, -0.2783103765422581, -0.30017426146810067, -0.23735694422069997, -0.15802705569807785, -0.1688744146997223, 0.00533368216211727, -0.2545781369382638, -0.28210347487274845, -0.2979168228680322, -0.3228351105624938, -0.3895784140998515, 0.4323790387934068, 0.17439008371288622, -0.12961415393892395, -0.223631490605527, -0.040224472420860025, -0.4264043621594098, -0.001900645929026723, -0.07466309859101727, -0.08665139450376103, -0.08169292404001283, -0.31617707504575066, -0.47420548422877573, 0.1502063550179713, 0.30508111820872585, 0.031032583278971515, -0.17852388186996393, -0.3371366681033834, -0.41780673457925843, -0.2023933346444835, -0.10605089260880618, -0.10771060808245636, -0.16037790997569346, -0.18698598726336257, -0.1735616521412524, -0.008242337244190878, -0.011400119798814501, -0.18767393274848132, -0.360175323324853, 0.011681766969516616, -0.1931417836124183] ideal offset: -0.16889353086013453
我們現在可以使用一些啟發式方法來嘗試估計最有可能演唱的音符序列。上面計算的理想偏移是一個要素 - 但我們也需要知道速度 (例如,多少個預測構成一個八分音符?) 以及開始量化的時間偏移。為了簡單起見,我們將嘗試不同的速度和時間偏移,並測量量化誤差,最後使用最小化此誤差的值。
def quantize_predictions(group, ideal_offset):
# Group values are either 0, or a pitch in Hz.
non_zero_values = [v for v in group if v != 0]
zero_values_count = len(group) - len(non_zero_values)
# Create a rest if 80% is silent, otherwise create a note.
if zero_values_count > 0.8 * len(group):
# Interpret as a rest. Count each dropped note as an error, weighted a bit
# worse than a badly sung note (which would 'cost' 0.5).
return 0.51 * len(non_zero_values), "Rest"
else:
# Interpret as note, estimating as mean of non-rest predictions.
h = round(
statistics.mean([
12 * math.log2(freq / C0) - ideal_offset for freq in non_zero_values
]))
octave = h // 12
n = h % 12
note = note_names[n] + str(octave)
# Quantization error is the total difference from the quantized note.
error = sum([
abs(12 * math.log2(freq / C0) - ideal_offset - h)
for freq in non_zero_values
])
return error, note
def get_quantization_and_error(pitch_outputs_and_rests, predictions_per_eighth,
prediction_start_offset, ideal_offset):
# Apply the start offset - we can just add the offset as rests.
pitch_outputs_and_rests = [0] * prediction_start_offset + \
pitch_outputs_and_rests
# Collect the predictions for each note (or rest).
groups = [
pitch_outputs_and_rests[i:i + predictions_per_eighth]
for i in range(0, len(pitch_outputs_and_rests), predictions_per_eighth)
]
quantization_error = 0
notes_and_rests = []
for group in groups:
error, note_or_rest = quantize_predictions(group, ideal_offset)
quantization_error += error
notes_and_rests.append(note_or_rest)
return quantization_error, notes_and_rests
best_error = float("inf")
best_notes_and_rests = None
best_predictions_per_note = None
for predictions_per_note in range(20, 65, 1):
for prediction_start_offset in range(predictions_per_note):
error, notes_and_rests = get_quantization_and_error(
pitch_outputs_and_rests, predictions_per_note,
prediction_start_offset, ideal_offset)
if error < best_error:
best_error = error
best_notes_and_rests = notes_and_rests
best_predictions_per_note = predictions_per_note
# At this point, best_notes_and_rests contains the best quantization.
# Since we don't need to have rests at the beginning, let's remove these:
while best_notes_and_rests[0] == 'Rest':
best_notes_and_rests = best_notes_and_rests[1:]
# Also remove silence at the end.
while best_notes_and_rests[-1] == 'Rest':
best_notes_and_rests = best_notes_and_rests[:-1]
現在讓我們將量化的音符寫成樂譜!
為了做到這一點,我們將使用兩個程式庫:music21 和 Open Sheet Music Display
# Creating the sheet music score.
sc = music21.stream.Score()
# Adjust the speed to match the actual singing.
bpm = 60 * 60 / best_predictions_per_note
print ('bpm: ', bpm)
a = music21.tempo.MetronomeMark(number=bpm)
sc.insert(0,a)
for snote in best_notes_and_rests:
d = 'half'
if snote == 'Rest':
sc.append(music21.note.Rest(type=d))
else:
sc.append(music21.note.Note(snote, type=d))
bpm: 78.26086956521739
[執行此程式碼] 使用 Open Sheet Music Display (JS 程式碼) 顯示樂譜的輔助函式
/tmpfs/tmp/ipykernel_33973/2305315633.py:3: DeprecationWarning: Importing display from IPython.core.display is deprecated since IPython 7.14, please import from IPython display from IPython.core.display import display, HTML, Javascript
# rendering the music score
showScore(sc)
print(best_notes_and_rests)
/tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/music21/musicxml/m21ToXml.py:510: MusicXMLWarning: <music21.stream.Score 0x7f9e28198580> is not well-formed; see isWellFormedNotation()
warnings.warn(f'{scOut} is not well-formed; see isWellFormedNotation()',
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object> ['C3', 'D3', 'E3', 'F3', 'G3', 'A3', 'B3', 'C4']
讓我們將音符轉換為 MIDI 檔案並聆聽。
若要建立此檔案,我們可以使用之前建立的串流。
# Saving the recognized musical notes as a MIDI file
converted_audio_file_as_midi = converted_audio_file[:-4] + '.mid'
fp = sc.write('midi', fp=converted_audio_file_as_midi)
wav_from_created_midi = converted_audio_file_as_midi.replace(' ', '_') + "_midioutput.wav"
print(wav_from_created_midi)
converted_audio_file.mid_midioutput.wav
若要在 Colab 上聆聽,我們需要將其轉換回 wav。一種簡單的方法是使用 Timidity。
timidity $converted_audio_file_as_midi -Ow -o $wav_from_created_midi
Playing converted_audio_file.mid MIDI file: converted_audio_file.mid Format: 1 Tracks: 2 Divisions: 1024 Track name: Playing time: ~16 seconds Notes cut: 0 Notes lost totally: 0
最後,聆聽音訊,該音訊是從音符建立的,音符是透過 MIDI 從預測的音高建立的,而音高是由模型推斷出來的!
Audio(wav_from_created_midi)
